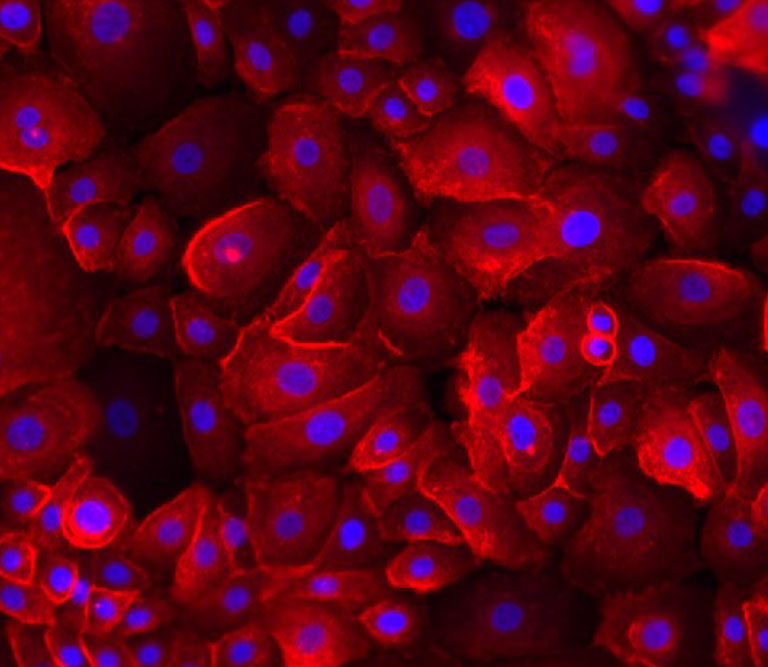
Keratinocytes are the main cellular component of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. They originate in the basal layer and undergo a process of differentiation, migrating upwards to form the protective stratum corneum. These cells play a vital role in skin barrier function, preventing water loss, shielding against environmental aggressors, and contributing to wound healing and immune responses.
As keratinocytes move through the epidermis, they produce keratin, a structural protein that reinforces the skin’s strength and resilience. They also secrete cytokines and growth factors, influencing immune defense and repair mechanisms. Beyond their protective function, keratinocytes are involved in interactions with melanocytes, influencing pigmentation, and working alongside fibroblasts to maintain skin integrity.